
Jong-Sung Yu
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Sicence & Technology, South Korea
Title: Highly effi cient oxygen-defi cient reduced Tio2-x for sunlight-induced water splitting for H2 generation
Biography
Biography: Jong-Sung Yu
Abstract
High effi ciency with stable performance and utilization of visible light is a key challenge to sunlight-induced photochemical generation of H2, the cleanest energy carrier. Recently, black TiO2-x materials were achieved by creating oxygen vacancies and/or defects at the surface using diff erent methods. Fascinatingly, they exhibited an extended absorption in VIS and IR as well as UV light, along with a band gap decrease from 3.2 (anatase) to ~1 eV. However, despite the dramatic enhancement of optical absorption of black TiO2-x material, it fails to show expected visible light-assisted water splitting effi ciency.
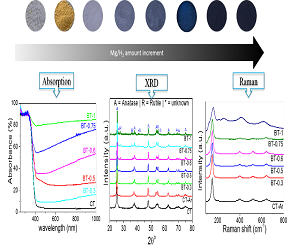
Therefore, a new reduced TiO2 material with optimized properties would be highly desired for visible light photocatalysis. Herein, we report H-doped reduced TiO2-x nanoparticles prepared by a controlled reduction via the simultaneous presence of two active reducing species, [Mg] and [H] in a confined microenvironment at the surface of TiO2. Th is new material exhibits outstanding activity (31.4 mmolg-1h-1) and excellent stability aft er Pt deposition for photochemical H2 generation from methanol-water in simulated sunlight. Th e excellent photoactivity of H:TiO2-x is attributed to the oxygen vacancies and H doping at the TiO2 surface generated by [Mg] and [H]. The photocatalyst works at wavelengths <700 nm and exhibits reasonable visible-light activity with a quantum yield of 17.8, 7.62 and 3.72% at 400, 420 and 454 nm, respectively, along with an exceptionally high turnover number (238680) with respect to Pt. Th is outstanding activity can be correlated with the extended absorption of visible light, perfect band position, presence of an appropriate amount of Ti3+ and oxygen vacancy and slower charge recombination.

